 +1 302-235-9792
+1 302-235-9792

- News
- Trimer-Based Gene Library Service – Enhancing Library Precision and Accuracy
Trimer-Based Gene Library Service – Enhancing Library Precision and Accuracy
Gene libraries are essential tools in molecular biology and genomics, widely used in gene function research, gene cloning, and drug screening. Conventional gene library construction methods, such as degenerate saturation mutagenesis using NNK or NNS degenerate primers, include 32 (4×4×2) codon combinations corresponding to 20 amino acids. This inevitably leads to codon redundancy, making it impossible to achieve equal-probability amino acid mutations and increasing the risk of introducing stop codons (TAG/TAA), thereby complicating the screening process.
The primer synthesis process used in the Trimer Gene Library differs from that of degenerate primers. Instead of synthesizing degenerate primers, it employs trimers as raw materials, adding three bases per cycle (corresponding to a single amino acid). A Trimer Gene Library contains a maximum of 20 codons, with each codon corresponding to one amino acid.By proportionally mixing Trimer primers, the amino acid composition and ratio can be precisely customized, eliminating the introduction of stop codons and unwanted codons. The actual amino acid distribution closely matches the intended design. Compared to traditional mutagenesis and degenerate synthesis methods, this approach significantly reduces the screening workload, helping to save both time and costs.As a result, the Trimer Gene Library is ideal for creating highly diverse and high-quality libraries.
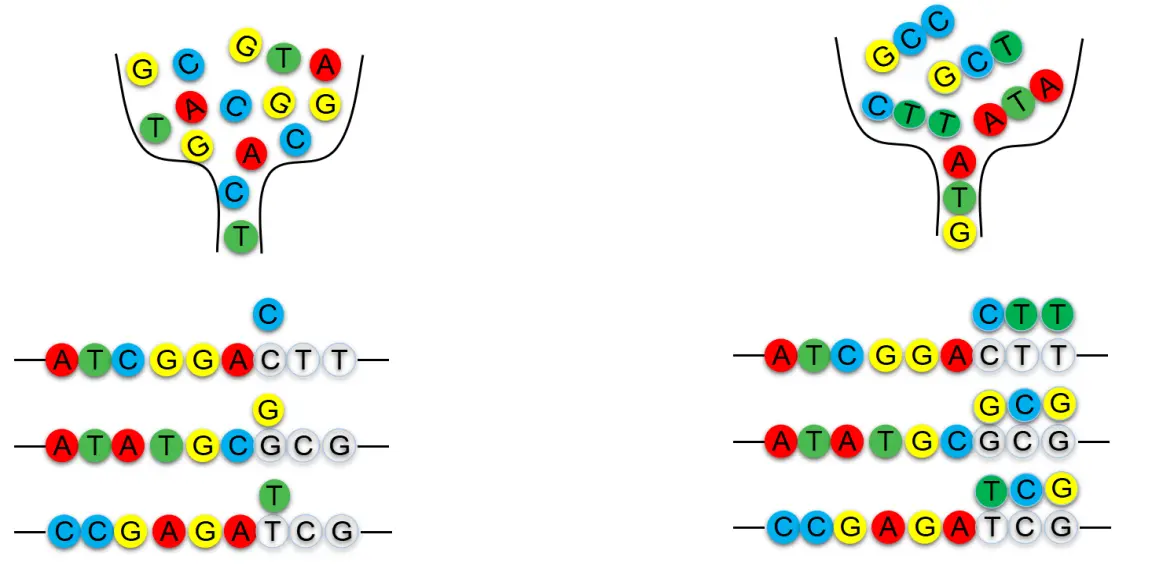
Degenerate Primer Synthesis
Trimer Primer Synthesis
Application Fields
Directed Evolution of Proteins
Antibody Engineering
New Drug Development
Gene Universal Trimer Gene Library Service
Gene Universal has a professional gene library development team and an advanced technology platform, with extensive experience in Trimer Gene Library construction. We offer one-stop services and customized solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Case Study 1: Equal-Proportion Amino Acid Distribution
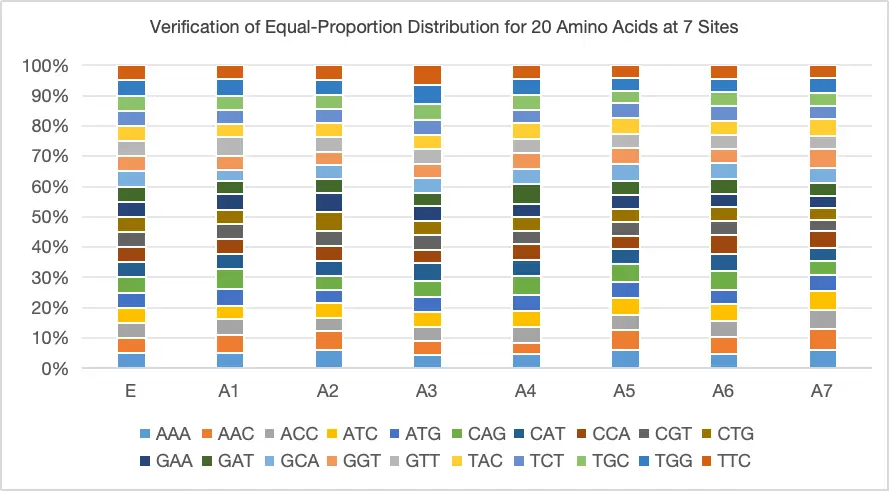
Supports Non-Equal Proportion Customized Mutations, the distribution of various amino acids closely matches the designed proportions.
Case Study 2: Non-Equal Proportion Customized Mutations
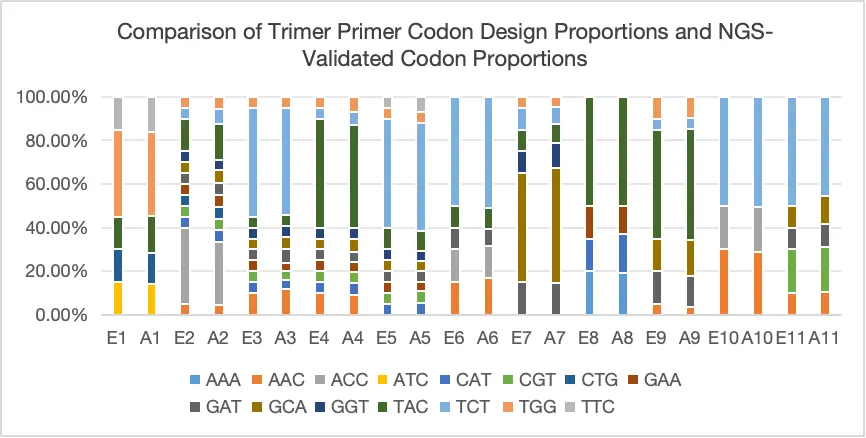
The Trimer Gene Library method enables controlled amino acid distribution, preventing the introduction of stop codons and unwanted amino acids while reducing frameshift mutations. This enhances the precision and accuracy of library screening. With the Trimer Gene Library, high-complexity libraries can be generated with exceptional accuracy. This approach significantly reduces screening workload, saving both time and costs while improving overall efficiency.
Trimer Primer Synthesis Service
Gene Universal offers Trimer Primer Synthesis services, ideal for constructing Trimer libraries and meeting your specific amino acid diversity and preference requirements at targeted sites.
Example:
5GCAACTTATTACTGTCAGCAA(X)5-8CYGWTCACGTTCGGACAGGG3
X Trimers=Y(50%)/S (10%)/G(10%)/A(5%)/F(5%)/W(5%)/H(5%)/P(5%)/V(5%)
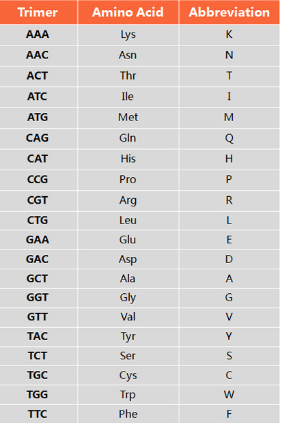
Trimer Codon-Amino Acid Mapping Table
|
Codon
|
Abbrev |
Amino Acid |
|---|---|---|
|
AAA |
K |
Lys |
|
AAC |
N |
Asn |
|
ACC |
T |
Thr |
|
ATC |
I |
Ile |
|
ATG |
M |
Met |
|
CAG |
Q |
Gln |
|
CAT |
H |
His |
|
CCA |
P |
Pro |
|
CGT |
R |
Arg |
|
CTG |
L |
Leu |
|
GAA |
E |
Glu |
|
GAT |
D |
Asp |
|
GCA |
A |
Ala |
|
GGT |
G |
Gly |
|
GTT |
V |
Val |
|
TAC |
Y |
Tyr |
|
TCT |
S |
Ser |
|
TGC |
C |
Cys |
|
TGG |
W |
Trp |
|
TTC |
F |
Phe |
|
Degenerate Bases
|
Codon |
Abbrev |
Amino Acid |
Number |
ID |
|
Codon |
Abbrev |
Amino Acid |
Number |
ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
R=A/G |
TTT |
F |
Phe |
2 |
1 |
ATG |
M |
Met |
1 |
37 |
|
|
Y=C/T |
TTC |
2 |
ACT |
T |
Thr |
4 |
38 |
||||
|
M=A/C |
TTA |
L |
Leu |
6 |
3 |
ACC |
39 |
||||
|
K=G/T |
TTG |
4 |
ACA |
40 |
|||||||
|
S=C/G |
CTT |
5 |
ACG |
41 |
|||||||
|
W=A/T |
CTC |
6 |
AAT |
N |
Asn |
2 |
42 |
||||
|
H=A/C/T |
CTA |
7 |
AAC |
43 |
|||||||
|
B=C/G/T |
CTG |
8 |
AAA |
K |
Lys |
2 |
44 |
||||
|
V=A/C/G |
TCT |
S |
Ser |
6 |
9 |
AAG |
45 |
||||
|
D=A/G/T |
TCC |
10 |
GTT |
V |
Val |
4 |
46 |
||||
|
N=A/C/G/T |
TCA |
11 |
GTC |
47 |
|||||||
|
TCG |
12 |
GTA |
48 |
||||||||
|
AGT |
13 |
GTG |
49 |
||||||||
|
AGC |
14 |
GCT |
A |
Ala |
4 |
50 |
|||||
|
TAT |
Y |
Tyr |
2 |
15 |
GCC |
51 |
|||||
|
TAC |
16 |
GCA |
52 |
||||||||
|
TGT |
C |
Cys |
2 |
17 |
GCG |
53 |
|||||
|
TGC |
18 |
GAT |
D |
Asp |
2 |
54 |
|||||
|
TGG |
W |
Trp |
1 |
19 |
GAC |
55 |
|||||
|
CCT |
P |
Pro |
4 |
20 |
GAA |
E |
Glu |
2 |
56 |
||
|
CCC |
21 |
GAG |
57 |
||||||||
|
CCA |
22 |
GGT |
G |
Gly |
4 |
58 |
|||||
|
CCG |
23 |
GGC |
59 |
||||||||
|
CAT |
H |
His |
2 |
24 |
GGA |
60 |
|||||
|
CAC |
25 |
GGG |
61 |
||||||||
|
CAA |
Q |
Gln |
2 |
26 |
TAA |
Stop Codon |
3 |
62 |
|||
|
CAG |
27 |
TAG |
63 |
||||||||
|
CGT |
R |
Arg |
6 |
28 |
TGA |
64 |
|||||
|
CGC |
29 |
||||||||||
|
CGA |
30 |
||||||||||
|
CGG |
31 |
||||||||||
|
AGA |
32 |
||||||||||
|
AGG |
33 |
||||||||||
|
ATT |
I |
Ile |
34 |
34 |
|||||||
|
ATC |
35 |
||||||||||
|
ATA |
36 |
64 Codon Standard Table
References
References 1: Bingrui S ,Xinrui W ,Tianyi Z , et al. Design, Screening, and Characterization of Engineered Phage Endolysins with Extracellular Antibacterial Activity against Gram-Negative Bacteria. [J]. Applied and environmental microbiology, 2023, 89 (7): e0058123-e0058123.
References 2: Sayous V ,Lubrano P ,Li Y , et al. Unbiased libraries in protein directed evolution [J]. BBA - Proteins and Proteomics, 2020, 1868 (2): 140321.

