 +1 302-235-9792
+1 302-235-9792
OVERVIEW
DNA libraries refer to a collection of large numbers of DNA sequences that have been cloned into vectors, researchers working in fields such as protein engineering, antibody engineering, enzyme engineering, synthetic biology, discovery biology, and structural biology can identify and isolate the DNA fragments interested for further study. Our library types include Site-directed Mutagenesis Library, Scanning Library, Randomized Library, Degenerated Library, and Truncation Library.
FEATURED SYNTHETIC DNA LIBRARIES
-
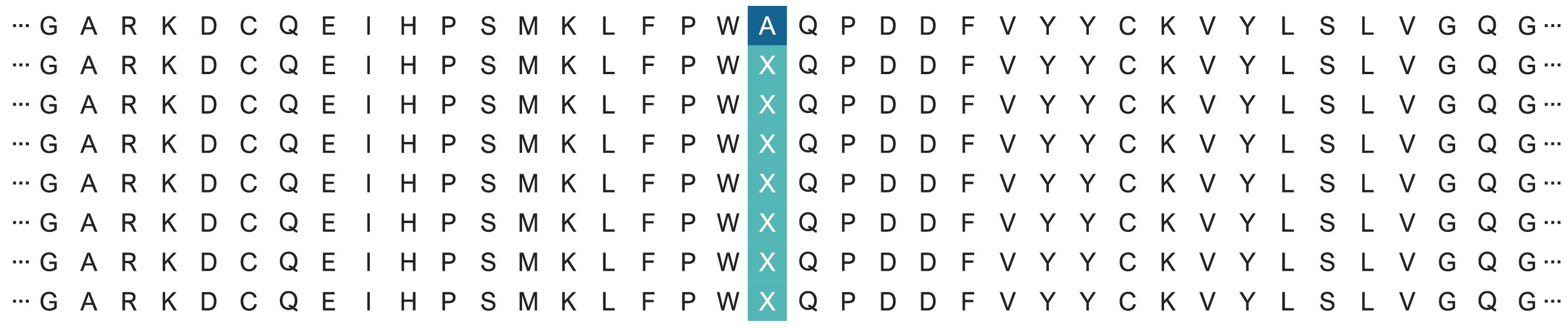
1. Site-directed Mutagenesis Library:
Site-directed mutagenesis library involves sequentially substituting a customer-determined amino acid position with all 19 other amino acids to generate a mutant library. This method enables scientists to conduct structural-functional analysis, examining the impacts of specific amino acid substitutions, both beneficial and adverse.
-
2. Scanning Library:
Scanning Library involves sequentially substituting specific residues within a customer-defined region with one specified residue via site-directed mutagenesis. Alanine and Cysteine scanning are two commonly utilized types of scanning libraries.

-
3. Randomized Library:
A randomized mutant library enables random amino acid substitutions within a user-defined region (e.g., ORF region within 200bp-1500bp). These proteins can be expressed and assayed for function to identify beneficial substitutions in protein engineering studies.

-
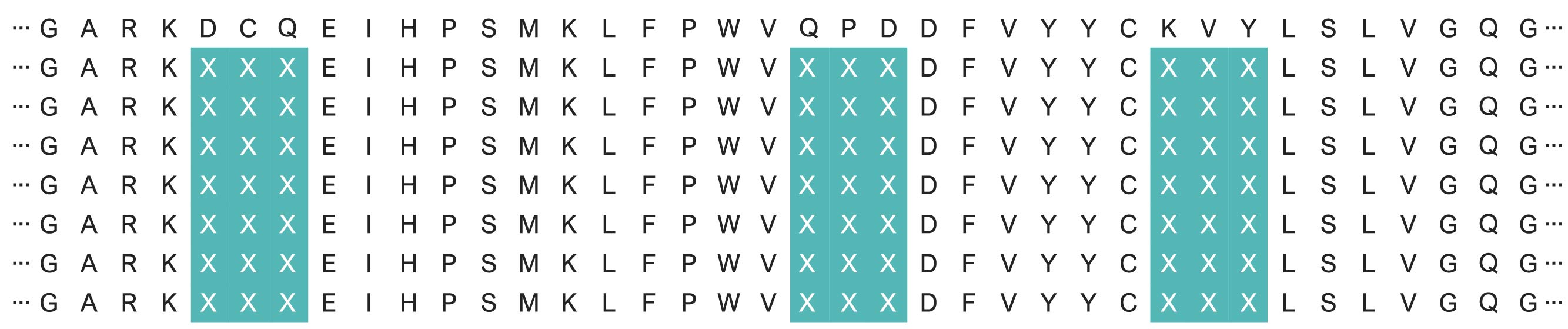
4. Degenerated Library:
Scientists can create a library of mutants by combining various genetic elements in multiple combinations. Gene Universal provides both traditional partially randomized (NNK/NNS) and completely randomized (NNN) mutant library services to support this endeavor.
-
5. Truncation Library:
A truncation library of mutants is constructed by trimming amino acids from either the N- or C-terminus (or both) of a protein around a specified core region. This enables scientists to pinpoint the core region responsible for protein function.

SERVICE DETAILS
| Mutant Type | Capacity | Quality Control | Deliverable |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Site-directed Mutagenesis Library |
Individual, 100% sequence-verified clones |
Certificate of Analysis (COA) : 1.Restriction digest map 2.Sequence trace data with alignment 3.Sequence files of the synthetic gene alone or subcloned into a vector |
2-5 µg of lyophilized plasmid DNA |
|
Scanning Library |
Individual, 100% sequence-verified clones |
Certificate of Analysis (COA) : 1.Restriction digest map 2.Sequence trace data with alignment 3.Sequence files of the synthetic gene alone or subcloned into a vector |
2-5 µg of lyophilized plasmid DNA |
|
Randomized Library |
Ready-to-clone PCR Fragment Library or Cloned Pooled Library Up to 109 variants |
Sequence verification of a pre-determined number of clones (with statistical analysis) based on library size |
PCR fragment Library: 2-4 µg of linear ds DNA Cloned pool Library: 1. 5-10 µg of lyophilized plasmid DNA 2.Glycerol stock of total library with up to 109 transformants |
|
Degenerated Library |
Ready-to-clone PCR Fragment Library or Cloned Pooled Library Up to 109 variants |
Sequence verification of a pre-determined number of clones (with statistical analysis) based on library size |
PCR fragment Library: 2-4 µg of linear ds DNA Cloned pool Library: 1.5-10 µg of lyophilized plasmid DNA 2.lycerol stock of total library with up to 109 transformants |
|
Truncation Library |
Individual, 100% sequence-verified clones |
Certificate of Analysis (COA) : 1.Restriction digest map 2.Sequence trace data with alignment 3.Sequence files of the synthetic gene alone or subcloned into a vector |
2-5 µg of lyophilized plasmid DNA |
If you have custom requests or require any pre-project consultation, please contact us at sales@geneuniversal.com
Online Request Submission
Have a question about sales or support? Our team is ready to help!


